Global spend on information security and risk management tools has shown a steady upward trend in the past years. The spend on enterprise software alone is estimated to grow to 557.4 billion dollars through 2022 as remote work environments become more pervasive—thanks to the COVID-19 pandemic. As organizations continue to equip themselves with the right technologies and skills to combat cyber threats, breaches still continue to occur risking heavy financial and reputational loss to businesses. In 2020, IBM estimated the average cost of a data breach at 3.86 million dollars.
According to a talk at RSA 2019 by security operations consultants from Palo Alto Networks, small organizations use 15 to 20 security tools, medium organizations use 50-60 tools and large organizations use as many as 130 tools! Using so many tools inevitably results in higher costs of ownership, increased complexity, and more technology for security teams to manage and master. Tech Target reported that many CISOs can’t keep up with the endless technology updates to their own security portfolios—as much as 50% of existing functionality actually goes unused—let alone the constant barrage of new controls.

Why Are There So Many Tools in Use? 🔗︎
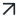
Organizational teams tasked with protecting the security systems of the organization are called a Security Operations Center (SOC). SOC teams tasks range from set up and configuration, monitoring of systems, and the detection, investigation, and remediation of unintended incidents.
SOC teams undergo multiple stages of evolution as they grow, and over time new tools are acquired to solve new and specific challenges. In addition, enterprise IT infrastructures are becoming increasingly complex as companies steadily move to cloud solutions, workforces become remote, and the use of mobile and inter-connected devices becomes more widespread, resulting in new security solutions.
Finally, we find that larger organizations will tend to have a decentralized SOC and multiple supporting teams, each with their own toolset. This leads to a sprawling number of tools, particularly in large organizations, which are often not integrated with each other.
Too Many Tools, Too Little Integration 🔗︎
It is apparent that there is a burgeoning number of technologies and vendors on the market, each adding new and more powerful capabilities to help SOCs and adjacent teams. A study by the SANS Institute found that “too many tools that are not integrated” was one of the key challenges faced by SOCs, next to a lack of skilled staff and the need for automation and orchestration.
Another enterprise study on “The State of the SOC” commissioned by Fidelis reported that integrated investigation across endpoints, servers, and networks remains a major challenge for SOCs. While the importance of integrated collaborative investigation remained unquestioned, practical implementation was found to be ineffective due to the tedious work required to tie information from all systems together into a single investigation.
A SOC should be built keeping the interoperability of applications in mind. Tools in a traditional cybersecurity stack tend to be disparate solutions that are difficult to integrate, manage, and use.
How SOC Teams Can Tackle Tool Fatigue 🔗︎
In this whitepaper, we take a look at the standard toolset of a SOC team and present the solution to tackle tool fatigue: Introducing interoperable tools to your SOC team.
Download this whitepaper and learn how to leverage your tool stack to its full potential while ensuring efficiency in the workflow.
Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn or subscribe to our email newsletter for more whitepapers, case studies, and SOC tips like this!

 4.5 rating
4.5 rating