Executive Summary 🔗︎
Ransomware is a type of software that encrypts users’ data, ensuring that they can no longer recover it without payment. It has been around since about 1989 and has become a very lucrative business with a bleeding impact on organizations: Financial cost of pay-out, loss of reputation, agencies’ fines, permanent data loss, operational loss, clean-up/damage repair costs. As ransomware attacks rise alongside the massive adoption of technology and cryptocurrency, they have also evolved to implement non-monetary extortion threats and RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) strategy to urge victims into submitting payments.
In this whitepaper, we will guide you through the anatomy of ransomware attacks—including the threat actors, their operational processes and roles, and more—as well as the investigative workflows, data, and tools that support effective ransomware investigations.
Key Takeaways 🔗︎
Understanding Ransomware Threats 🔗︎
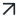
Although it has been the most remarkable cyberthreat in the last years, ransomware is not something new in the cybersecurity arena: The first malware asking for a ransom payment dates back to 1989. The invention of Bitcoin in 2008 (facilitating anonymous payments), the professionalization of cybercrime growing up heavily a few years later (strong collaboration and exchange in dark web hacking forums and markets), and the massive adoption of technology (with relevant vulnerabilities and high-impact exploits from time to time) has probably generated the “perfect storm” for them.
Ransomware, as a malware specimen, is a relatively simple piece of software that encrypts a victim’s data, making it theoretically unrecoverable, and demanding payment in exchange for recovery. It is mainly used by threat actors during the last stage of a network compromise. This means that, before its detonation, an initial entry vector was abused, and several steps were taken afterward to silently pivot and land into other highly relevant assets in the organization. During that breach, attackers will be trying to obtain enough privileges to launch data encryption and wipe everything out, including mirrored data and online backups, even hosted in alternative systems for business continuity purposes. It must be noted that their extortion activities do not just stop at asking a ransom for data recovery, but also heavily pressuring victims by threatening to leak stolen information, including customer data, intellectual property, etc.
IBM Ponemon Institute states that the average cost of a ransomware breach in 2021 was estimated at $4.62 million. We are talking about a very lucrative business with a bleeding impact on organizations: Financial cost of pay-out, loss of reputation, agencies’ fines, permanent data loss, operational loss, clean-up/damage repair costs.
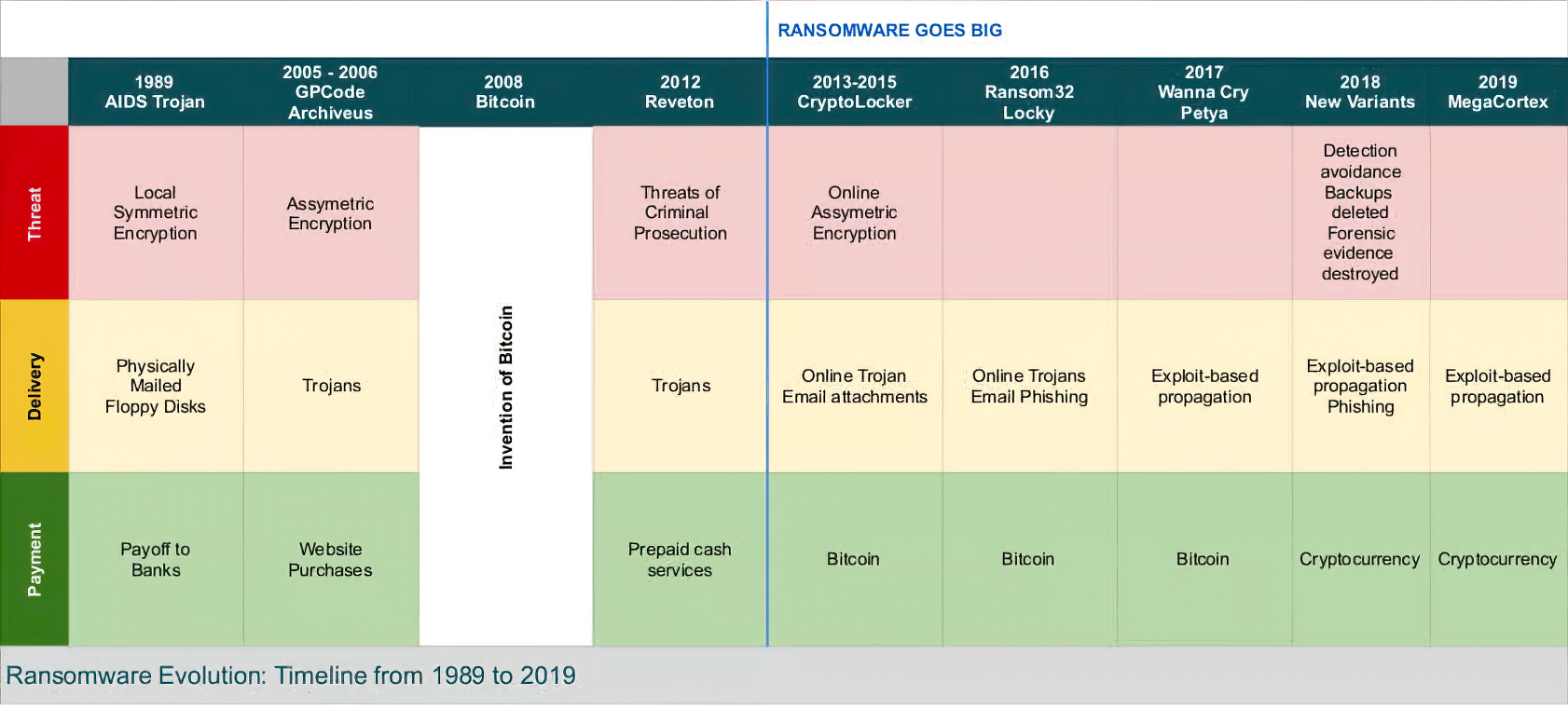
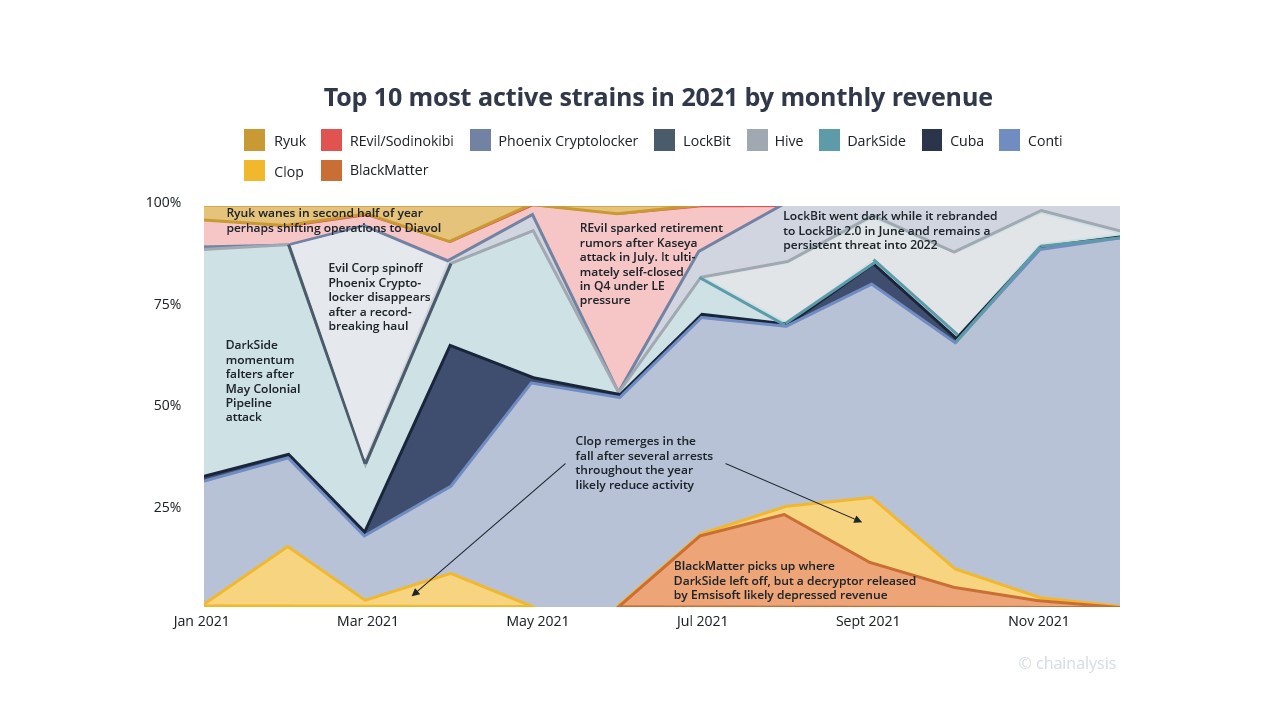
Chainalysis states in their 2021 report that there were more active ransomware strains than any other year, at least 140 of them received payments from victims at any point in 2021, compared to 119 in 2020, and 79 in 2019. The same study indicates that ransomware payment size was over $118,000 in 2021, up from $88,000 in 2020 and $25,000 in 2019, with some large payments such as the record $40 million received by Phoenix Cryptolocker. One reason for the mentioned increase in ransom sizes is ransomware attackers’ focus on carrying out highly targeted attacks against large organizations.
Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) & RaaS Players 🔗︎
As you will notice, there are many stages and different tools involved in a ransomware attack. The criminal hacking industry, as in any other software and services one, requires specialization and a strong partnership program as the most reasonable step to compete in this business. Nowadays, this is no longer a “Blue Ocean” as there are many threat actors competing to compromise a big ecosystem.
The most common trend in this ecosystem is following a collaborative operational model known as Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) with three clear roles: Operators, Affiliates, and Initial Access Brokers (IABs).
Download this whitepaper now to learn more about: 🔗︎
- RaaS attack groups and the roles of Operators, Affiliates, and Initial Access Brokers
- Attack trends of RaaS and their Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
- The 6 aspects of a ransomware investigation
- Top OSINT Tools and data providers for ransomware investigations
Download the resource
Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn and sign up to our email newsletter, so you don’t miss out on updates and news!
Happy investigating!