In the world of cybersecurity, like technology, threats are ever-evolving. This constant shift means vulnerability risk assessments must be integral to your organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
What are Vulnerability Risk Assessments? 🔗︎
Risk management is something that your organization is expected to implement to meet the objectives of Annex A.12.1 of ISO 27001. As part of your organization’s responsibilities, it will include assessing the risks.
Organizations conduct vulnerability risk assessments to identify, prioritize, and remediate potential risks in their digital infrastructure. These evaluations are a critical part of the lifecycle of an organization’s vulnerability management process.
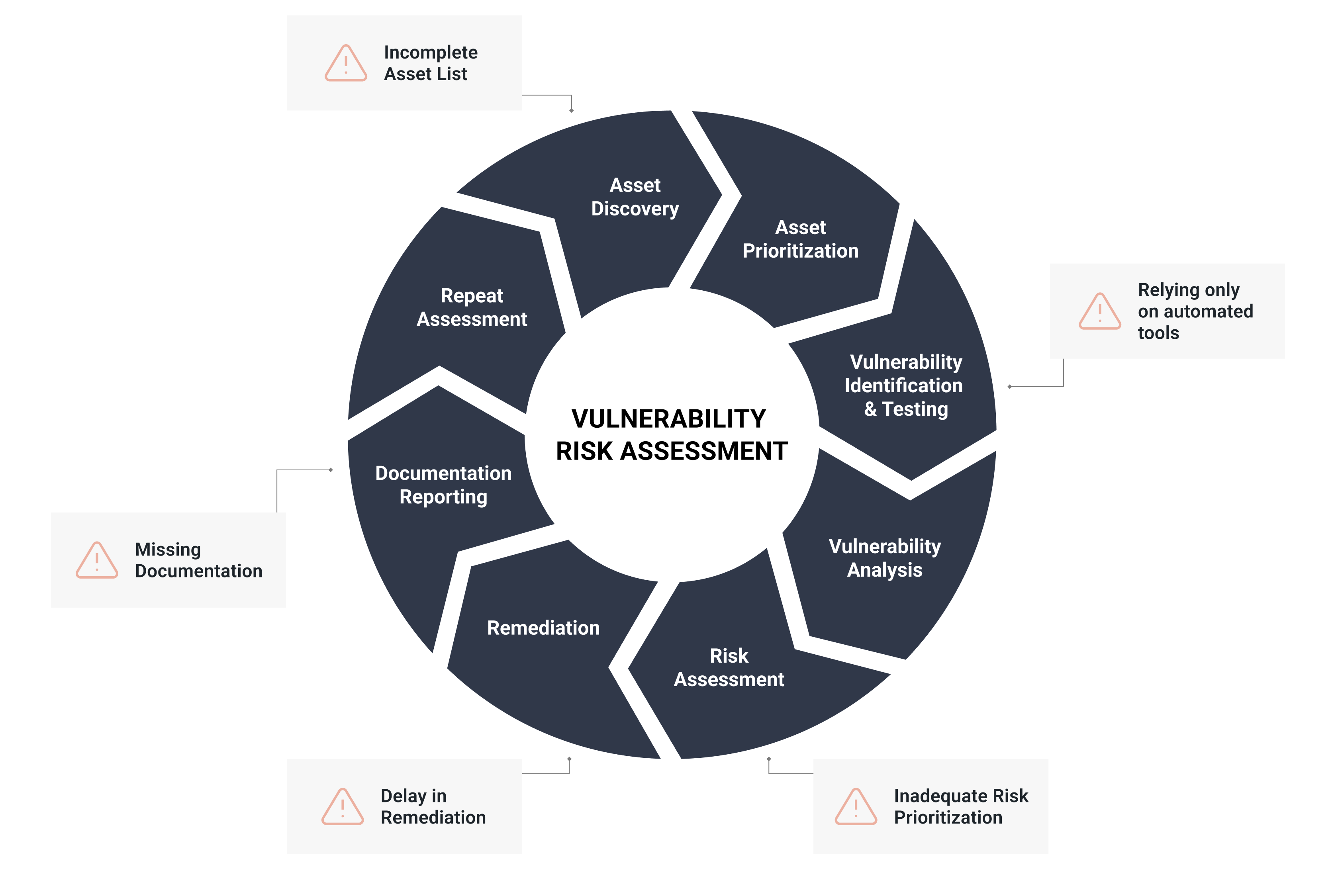
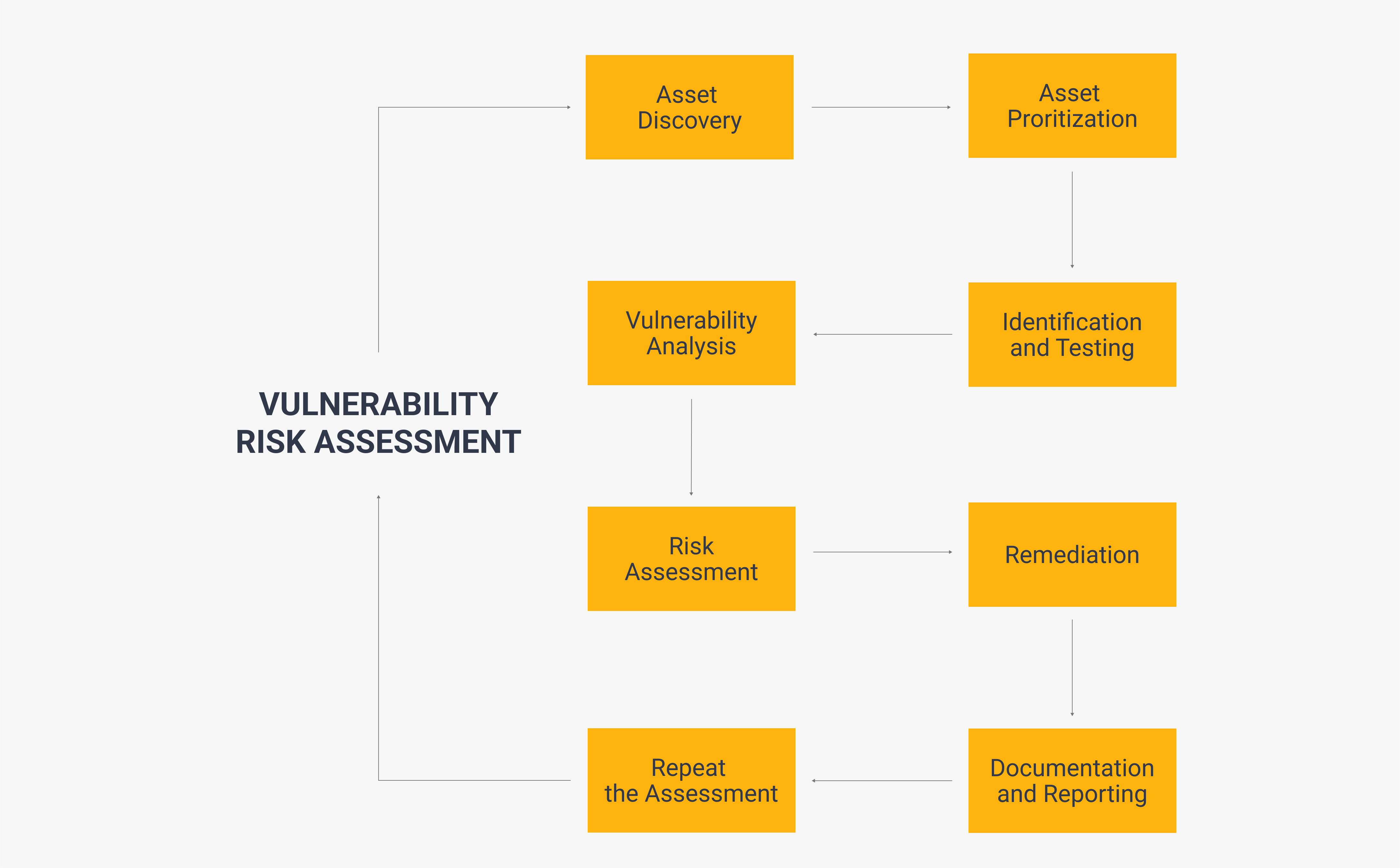
The main goal of a vulnerability risk assessment is to uncover weaknesses that could potentially be exploited by cyber attackers. This can be done in eight steps:
Asset Discovery: Asset Prioritization: Vulnerability Identification and Testing: Vulnerability Analysis: Risk Assessment: Remediation: Documentation and Reporting: Repeat the Assessment:
Though the steps involved in conducting one of these assessments vary between organizations, you can use these steps as a basic template to carry out your own.
What Pitfalls to Avoid in Vulnerability Risk Assessments and How OSINT Can Help 🔗︎
Conducting vulnerability risk assessments requires a keen understanding of potential errors that might arise during the process. When overlooked, these common pitfalls could lead to missing critical vulnerabilities or wasting time on irrelevant clues.
To assist you in identifying, classifying, prioritizing, and addressing system vulnerabilities, we have prepared a comprehensive PDF available for download.
This whitepaper will answer the following questions:
- What are the five most common pitfalls to avoid when performing vulnerability risk assessments?
- What are the best practices for conducting vulnerability risk assessments?
- How can open-source intelligence (OSINT) be applied in vulnerability risk assessments?
Download the PDF now to access the answers and enhance your vulnerability risk assessment capabilities.
Download the resource
We hope this whitepaper was helpful for you and your team to understand the importance of vulnerability risk assessments, avoid common mistakes, and conduct your own assessment using OSINT.
Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, and Mastodon, and sign up to our email newsletter, so you don’t miss out on updates and news!
Happy investigating!
Mario Rojas 🔗︎
Mario Rojas is a former Cyber Security and Threat Intelligence Subject Matter Expert at Maltego with more than 14 years of experience in the cybersecurity field. His expertise in open-source intelligence (OSINT) allows him to effectively map and visualize complex relationships and connections between entities, from IP addresses and domain names to social media profiles and Darkweb forums.

 4.5 rating
4.5 rating