With cyber threats and attack methods evolving in complexity, companies can no longer only work on a traditional and reactive basis but utilize insights from past incidents and current alerts to swiftly identify and address potential future threats. In this context, Maltego emerges as a critical platform for helping companies deal with the complexities of streamlining the entire lifecycle of threat intelligence, from collection and processing to analysis as part of their advanced security measures. Moreover, adopting these advanced security measures has become essential for businesses to protect their digital assets.
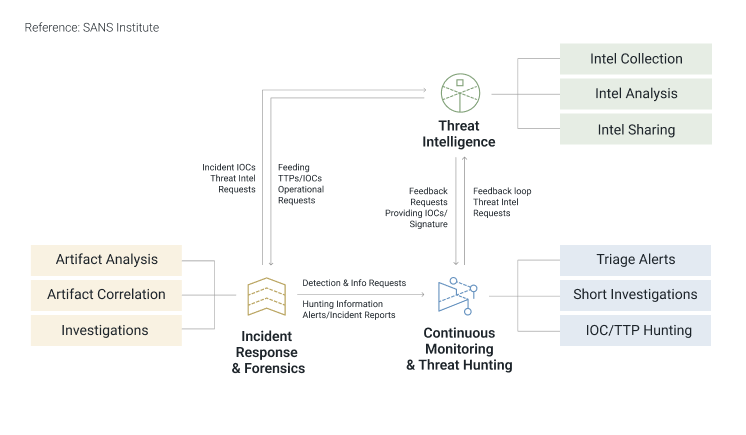
That is why businesses are turning to incident observations and cyber threat intelligence (CTI) to enhance their understanding of security events, allowing them to anticipate and proactively defend against future threats. CTI, in particular, plays a critical role in refining digital forensics and enhancing the incident response process, but it is still described as a nascent and fast-developing field.
In this article, we will cover foundational concepts and the application of cyber threat intelligence, a field shaped significantly by governmental and military organizations over the years. Additionally, we provide a handbook that your threat intelligence team can use to replicate the investigative process using Maltego, available for download.
What is Cyber Threat Intelligence? 🔗︎
In cybersecurity, threat intelligence refers to the data an organization collects, processes, and analyzes to better understand the motives, targets, and attack behaviors of threat actors, which can assist the decision-making process.
The fact that cybersecurity is increasingly recognized as a priority business risk, along with the growing variety and maturity of products, and factors such as regulatory requirements, are all driving the demand for cyber threat intelligence services. Let’s examine different types to determine the level of cyber threat intelligence your team would need.
Levels of Cyber Threat Intelligence 🔗︎
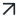
Cyber threat intelligence can be categorized into four levels:
- Strategic Threat Intelligence: It is high-level information including real-life factors such as economic conditions, political climates, the business impact of risks, and emerging trends in attack methodologies. Sources such as whitepapers, policy documents, and publications contribute to this knowledge base, aiming to enlighten non-technical stakeholders such as High-level executives and management.
- Operational Threat Intelligence: It is high-level but actionable information including the timing, objectives, and specific methods utilized by threat actors. It equips cybersecurity teams with the foresight needed to predict attacks and understand the schematics behind threat actors’ operations, particularly useful for threat hunters and incident responders. It covers specifics on attack vectors, like domains employed to control comprised systems, and information from external sources like the dark web, all to facilitate the assembly of TTPs.
- Tactical Threat Intelligence: It is information that outlines the TTPs employed by threat actors, utilizing frameworks like Mitre ATT&CK to track internal threat information feeds such as network traffic data. It provides a technical context that allows IT admins and SOC managers to detect system breaches or familiarize themselves with prevalent attack strategies. Furthermore, this information supports the improvement of security measures and the protection of businesses.
- Technical Threat Intelligence: It is information that includes specific technical indicators or evidence of threat actor’s tools and infrastructures, aimed at SOC staff to block malicious activities. Such information can include identified malicious IP addresses, phishing email subject lines or content, rogue URLs, or samples of malware and exploits. For example, if adversaries leverage corporate emails as an entry point into an organization (as identified through tactical threat intelligence), the specific email subject lines used would be classified as technical threat intelligence.
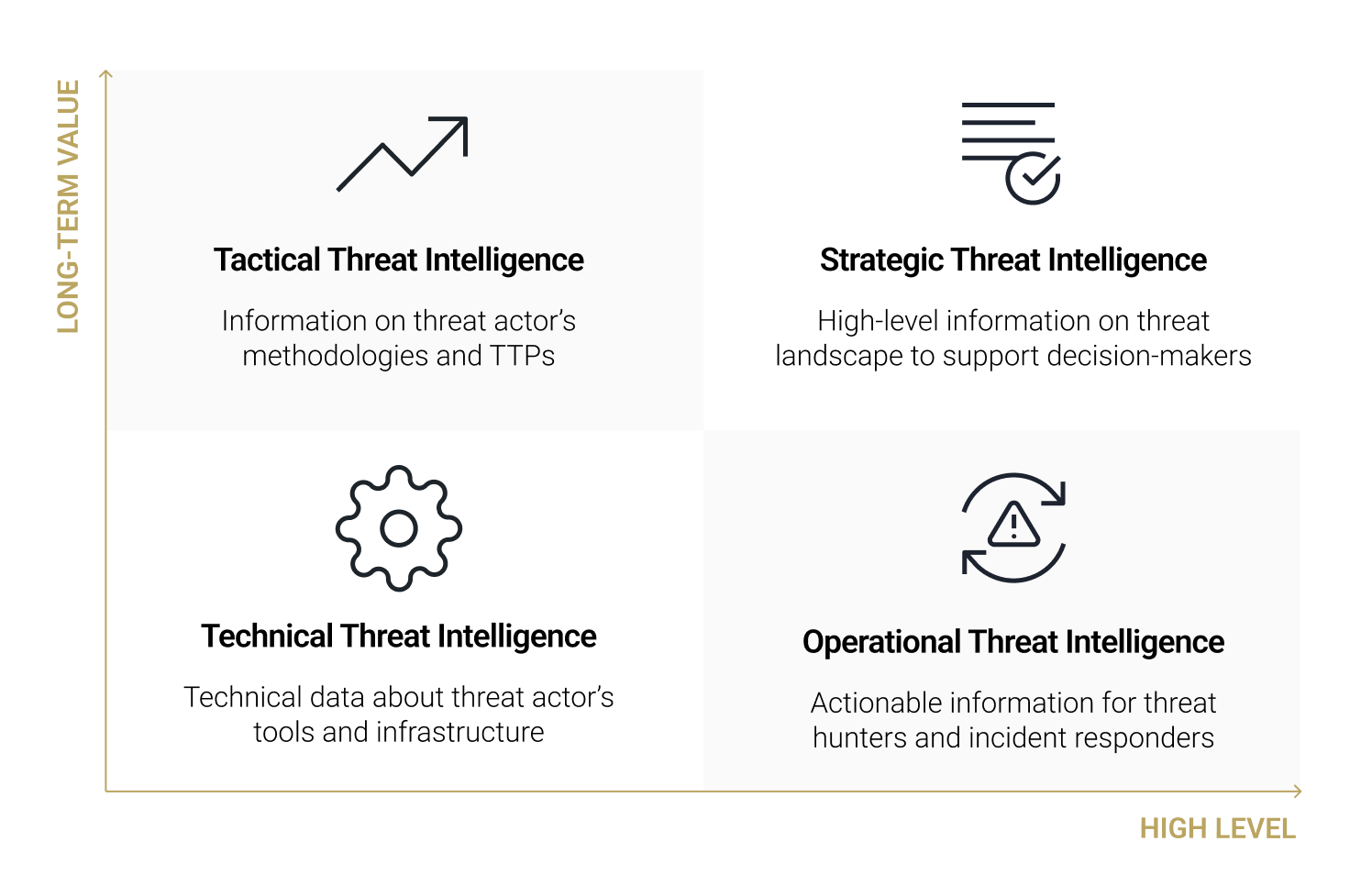
With this categorization in place, each operational team and individual can access the most relevant intelligence to their role. The goal of categorizing threat intelligence is to facilitate the identification and mitigation of risks, potentially even leading to the attribution of actors, given their diverse motivations and targets. For example, a bank may request its threat intelligence team to create reports on well-known, persistent cybercriminal groups in the industry to avoid becoming their target. Below are the typical motivations and targets associated with different types of cyber threat actors.
Lifecycle of Cyber Threat Intelligence 🔗︎
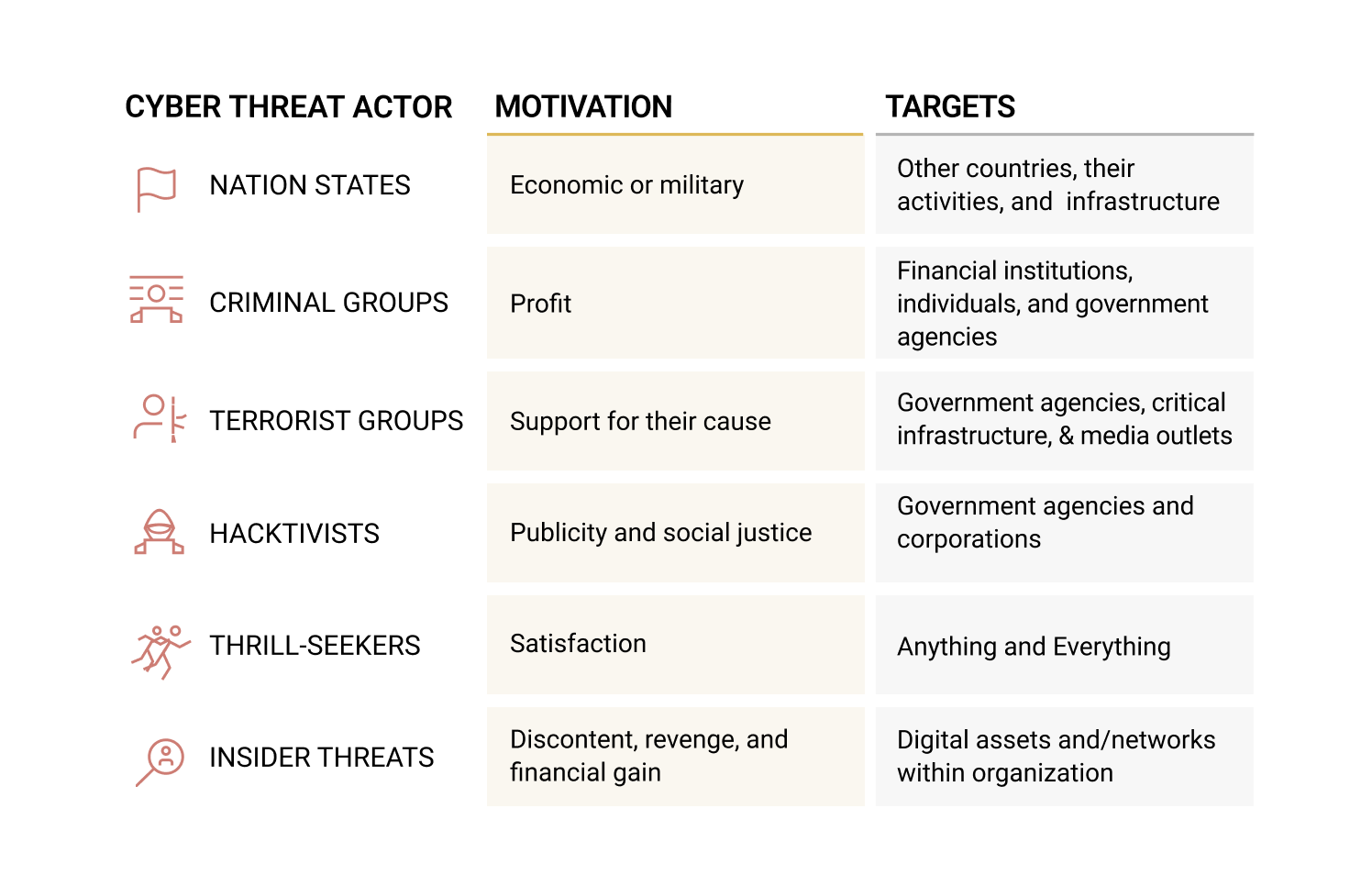
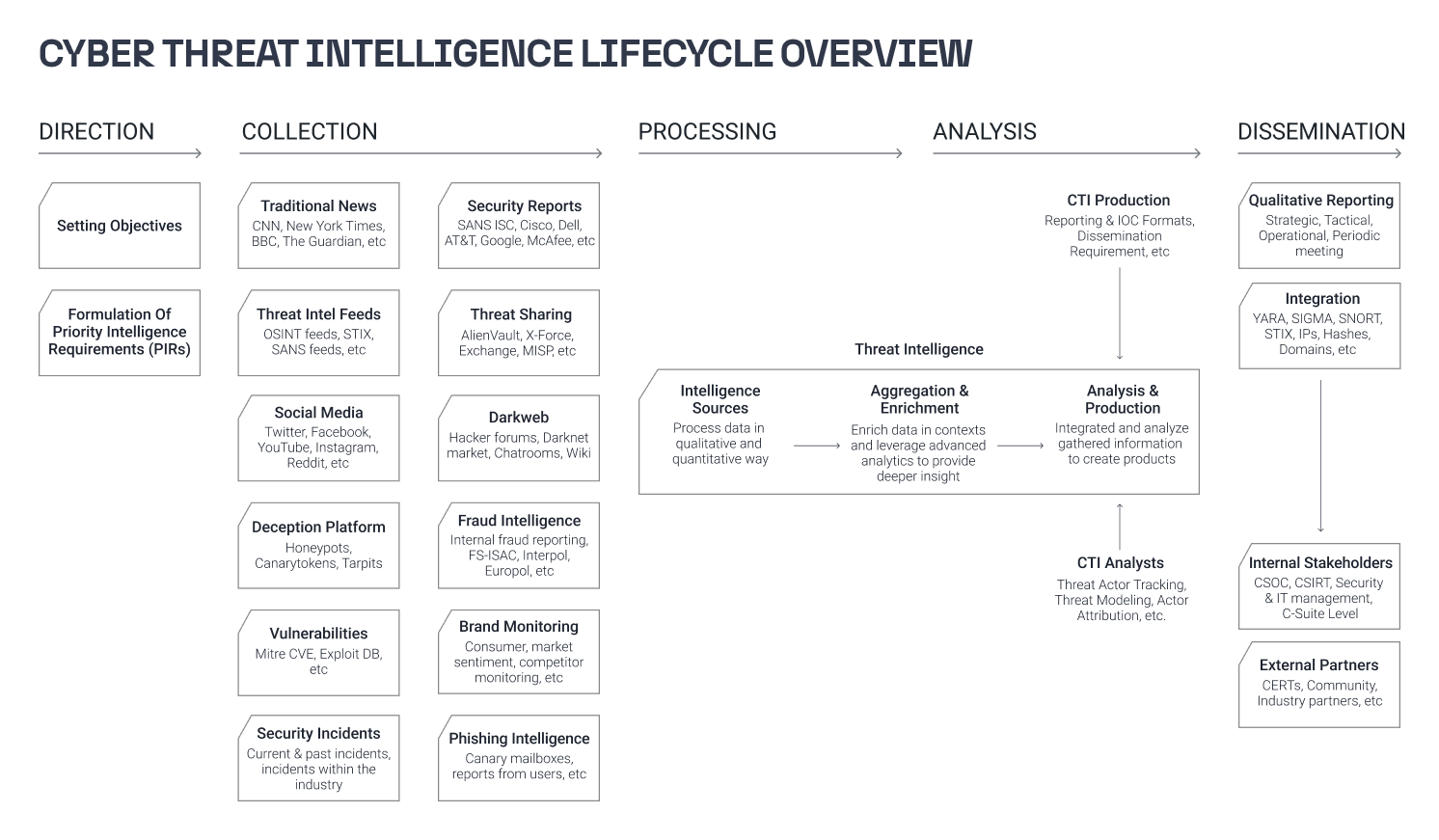
Numerous approaches to cyber threat intelligence exist, tailored to the specific requirements and priorities of the teams and different cases. However, the most widely adopted lifecycle model of cyber threat intelligence is one that has been developed through decades of intelligence efforts by government and military organizations like the CIA and the NSA. This model outlines the process of developing raw information into finished intelligence in six essential phases: Direction, Collection, Processing, Analysis, Dissemination, and Feedback.
Access the cheat sheet provided below to gain a comprehensive understanding of the six phases of the threat intelligence cycle. It includes examples and key considerations, and showcases Maltego in action, demonstrating how your team can enhance the efficiency of the threat intelligence lifecycle, from data collection and processing to analysis, all through the use of Maltego.
Key Use Cases Involving Cyber Threat Intelligence 🔗︎
Tailoring cyber threat intelligence to align with the specific requirements of each function and organization is crucial. Possessing a sophisticated level of threat intelligence empowers stakeholders to make swift, well-informed decisions. Additionally, it enables security professionals to more accurately grasp the decision-making processes of threat actors, facilitating earlier detection of threats and the implementation of automated responses. This approach also allows for the evaluation of the efficacy of existing security measures. Let’s first find out how it can benefit each function:
Security professionals utilize:
- Technical Threat Intelligence to proactively hunt for threat actors who bypass detections, investigate security alerts, and locate forensic evidence.
- Tactical Threat Intelligence to test their security technologies and processes, fine-tune tools, and lessen the gaps in their security controls.
- Operational Threat Intelligence to prevent or respond to planned attacks, create rules and signatures for detection alerts, and be proactive in vulnerability and patch management.
Stakeholders utilize:
- Strategic Intelligence to understand the likelihood of data breaches during risk assessments, set up the company’s cybersecurity stance and budget, as well as gauge the company’s compliance capabilities with regulations.
Download the Handbook for Expert Insights! 🔗︎
In our Cyber Threat Intelligence Handbook, we present the investigative playbook of five commonly known use cases, providing scenarios to demonstrate how you can utilize Maltego for cyber threat intelligence:
- Threat Intelligence Collection
- Malware Infrastructure Tracking
- Vulnerability and Attack Surface Assessment
- Threat Actors Profiling
- Attacks and TTPs Analysis
Additionally, you can also find out different methodologies of cyber threat intelligence such as mapping the threats to the MITRE ATT&CK framework and the diamond model of intrusion analysis. It also includes tips on various tools and the steps of setting up Maltego on your devices. If you haven’t used Maltego yet, now is the perfect opportunity to discover our organization plan for CTI designed specifically for your team!
Download the handbook to make your threat intelligence analysis effortless!
Download the resource
Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn and sign up for our email newsletter, so you don’t miss out on updates and news!
Happy investigating!