Cryptocurrency has seen enormous growth in the world economy. However, this has paved the way for criminal activity on the blockchain, which is why it is becoming increasingly important to trace and investigate transactions in different cryptocurrencies. The tools to obfuscate criminal cryptocurrency transactions are constantly evolving and luckily, so are the tools to trace them. In this whitepaper, Maltego and our experts give you an overview of how criminals obfuscate cryptocurrency and list out 7 most useful tools for cryptocurrency investigations. Executive Summary 🔗︎
Key Takeaways 🔗︎
Table of Content 🔗︎
- Criminal Activities on the Cryptocurrency Blockchain
- 3 Ways How Criminals Obfuscate Cryptocurrency Movements
- 7 Useful Data Providers and OSINT Tools for Tracing Cryptocurrency Movements
Since its launch in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin has seen its market capitalization rise from around 1 billion in 2013 to more than 1 trillion in 2021. While this explosive growth was taking place, a flurry of other cryptocurrencies was born. And, while Bitcoin remains the crypto coin with the highest market cap (and by far!), Ethereum and some others found success as well. As a result, today’s cryptocurrency transactions are complex, numerous, and continue to grow in volume.
To be able to investigate cryptocurrency transactions, one must understand how they differ from transactions made using fiat currencies, like dollars or euros. Given that each cryptocurrency can have its own set of evolving protocols defining these transactions, it quickly becomes an important aspect of the investigator’s job to keep up with the technology. For example, the Bitcoin “Taproot” update from last November introduced new mechanisms to Bitcoin, some of which improved the user’s privacy.
Some concepts, like smart contracts or the fact that a transaction can have multiple input and output addresses, are not self-evident and require that the investigator dives into the cryptocurrency they want to investigate before thinking of tracking its transaction.
Criminal Activities on the Cryptocurrency Blockchain 🔗︎
Why would one need to track cryptocurrency transactions? Well, while the popularity of cryptocurrencies grew, so did their usage. While there is a lot of legitimate usage for cryptocurrency, criminals also saw an opportunity in the decentralization and the relative anonymity offered by some cryptocurrencies. For example, according to a 2021 paper by Igor Makarov and Antoinette Schoar (London School of Economics and the National Bureau of Economic Research), “Illegal transactions, scams, and gambling together make up less than 3% of volume” of the Bitcoin transaction worldwide
Even if 3% seems like a small number, it should be noted that according to Binance, “in 2021, the Bitcoin network processed about $489 billion per quarter”, which means there are potentially billions of dollars of ill-gotten cryptocurrency being processed every year.
Tracking these ill-gotten funds can lead to the identification of the criminals moving said funds around and, sometimes, it may even lead to their recovery, as what happened during the Colonial Pipeline hack where the FBI was able to recover $2.3 million worth of Bitcoin. After the Bitcoin was seized, Deputy Attorney General, Lisa O. Monaco, made the subsequent declaration: “Following the money remains one of the most basic, yet powerful tools we have.”
3 Ways How Criminals Obfuscate the Trail of Bitcoin 🔗︎
Being able to track funds through cryptocurrency transactions is an important mean used by authorities to prevent and detect possible instances of money laundering. It is also something done by cryptocurrency exchanges—places used to buy and sell cryptocurrency in exchange for fiat currencies—to avoid unknowingly participating in organized crime and terrorism financing.
Several online free tools such as Blockchair, Etherscan and Ethplorer, exist that allow you to list the transactions linked to any given address in the most popular cryptocurrencies. These blockchain explorers offer an interface to visualize the information saved in the blockchain, namely the input and output addresses, the amount of the transactions, and the time of the transactions. However, this information alone may not be sufficient because investigators must put all the different bits of data together and find their correlations..
Let’s take Bitcoin as an example. Every transaction is available on the blockchain, a distributed public ledger that anyone can consult. Since regulated crypto exchanges have a KYC (Know Your Customer) duty, they by law should know the identity of people withdrawing funds using their services. To avoid having illegal funds traced back to them, criminals will use several methods to obfuscate the trail of Bitcoin. Here are some of these methods.
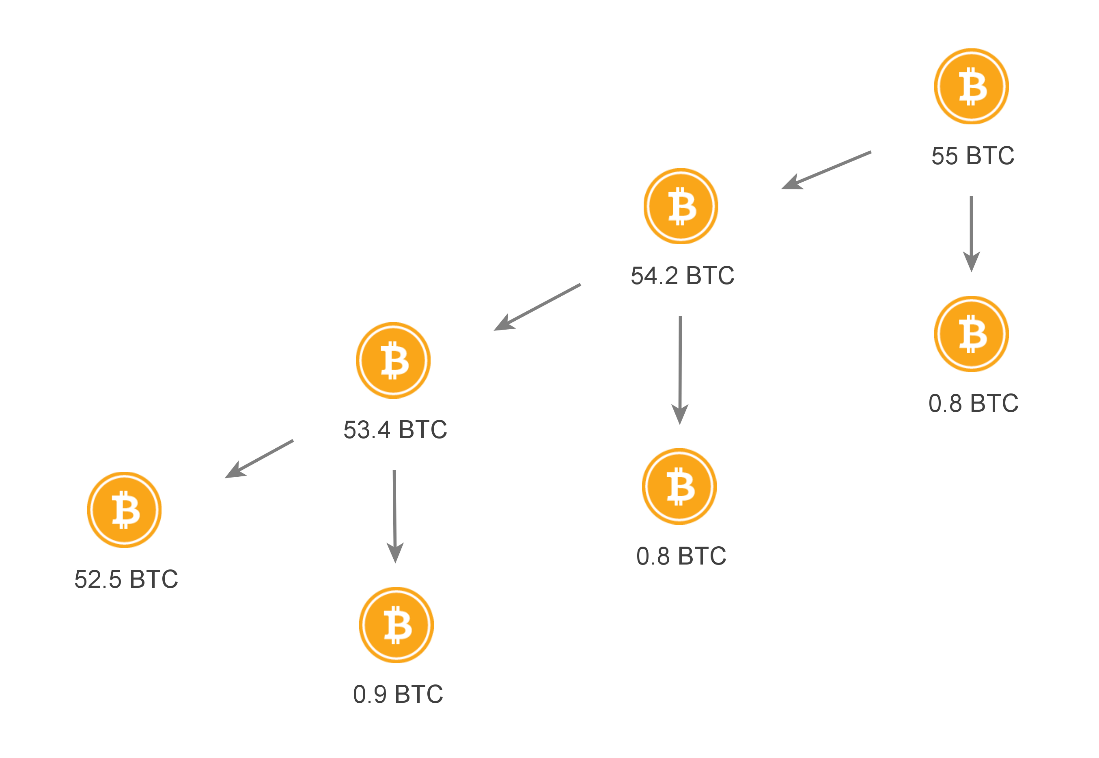
Peeling Chains 🔗︎
A peeling chain is a pattern commonly used to hide where a fairly big amount of coins is going. It usually starts off with a large number of coins concentrated in one address. This address will then send its money to two addresses. Transferring almost all the coins to the first address and the remainder to the second address. Then the process repeats itself until no money is left to “peel off”. Disseminating small amounts of money in many addresses makes it less likely to raise red flags for exchanges and other actors looking for money laundering. It also makes it more difficult for investigators to follow the money trail since it is split across multiple addresses.
Tumblers and Coinjoins 🔗︎
Tumblers are services that will attempt to anonymize your Bitcoin by bouncing them around the blockchain and mixing them with other Bitcoins while using different patterns to make it difficult to link a spender to a recipient. Using them is not strictly illegal, but several Bitcoin Tumbler operators have been arrested for money laundering amongst other criminal offenses. A coinjoin is a method used to combine multiple Bitcoin payments into a single transaction. This way, several spenders can associate to merge their Bitcoin and have them redistributed appropriately to the right recipients. This arrangement makes associating a spender with its recipient(s) quite difficult.
Chain Hopping 🔗︎
Chain hopping is the act of exchanging your coins from one type of cryptocurrency to another. For example, one could exchange their Bitcoin for an equivalent amount of Monero to take advantage of the privacy features built into it. Chain hopping can be done using a traditional exchange or a specialized website.
Even though there are legitimate uses for tumblers and coinjoins, exchanges are becoming more and more reluctant to process coins that have been through these services, for fear of participating in money laundering. This can ultimately complicate the cash out process.
7 Useful Data Providers and OSINT Tools for Tracing Cryptocurrency Movements 🔗︎
As we have seen, tracking cryptocurrency funds across different transactions is necessary, and Blockchain explorers are tools freely available online that can help you do so. However, their use of text to display transactions makes it difficult to follow the money when any number of obfuscation methods have been used.
With its graphical approach, Maltego is perfect for visualizing complex cryptocurrency transactions. Here is a selection of the most useful data integrations in Maltego to investigate cryptocurrency payments. The list is in alphabetical order and doesn’t indicate any ranking or preference.
Download this whitepaper for detailed descriptions and evaluations of the cryptocurrency data provided by each provider listed above.
Download the resource
Don’t forget to follow us Twitter and LinkedIn and sign up to our email newsletter to stay updated on new use cases, tutorials, and event information!